Solar radiation sensors are important tools for measuring sunlight intensity. They are vital for many uses, like solar energy monitoring and agricultural management. Installing these sensors correctly is crucial to ensuring accurate readings and optimal performance.
In this guide, we will show you how to install a solar radiation sensor. We will also give tips for fixing common installation problems.
Finally, we will explain how to connect these sensors to your current monitoring systems. If you are installing a sensor, this guide will help you. Useful for solar farms, greenhouses, and environmental monitoring.

Before diving into the installation process, it’s important to understand why proper setup is essential:
Accurate Readings: Incorrect installation can lead to inaccurate solar radiation data, affecting system performance and decision-making.
Longevity of the Sensor: Proper installation ensures that the sensor remains in good condition and functions reliably over time.
Optimized Performance:
Placing the sensor correctly helps it measure solar radiation levels accurately. This ensures the best efficiency in solar power systems and plant growth in greenhouses.
The location of the solar radiation sensor is critical to obtaining accurate measurements. Place the sensor where it receives direct sunlight for most of the day. There should be little shading from trees, buildings, or other objects.
Key Considerations:
Avoid Obstructions: Ensure the sensor is free from any objects that could block sunlight.
Elevated Position:
To get accurate readings, install the sensor higher up. Make sure it is clear of nearby objects that could cause shading.
Representative Location:
Put the sensor in a spot that best shows the area you are watching, like on a solar farm or in a field.
Once you’ve selected the ideal location, it’s time to mount the sensor. Most designers create solar radiation sensors for mounting on a flat surface, pole, or bracket.
Installation Tips:
Ensure Proper Tilt:
If your sensor is designed to measure solar radiation at specific angles, ensure that it is tilted correctly. For example, you should place a horizontal pyranometer flat. A tilted sensor should match the angle of the surface you are measuring.
Mount Securely: Use a strong, weatherproof mounting bracket to secure the sensor. Make sure the sensor remains stable, even in high winds or adverse weather conditions.
Check Orientation:
Some sensors, especially those made for certain measurements, may need to face a specific direction. For example, they might need to point true south in the Northern Hemisphere.
Solar radiation sensors often require a power supply or connection to a data logger or monitoring system. Ensure that you follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for connecting the sensor to the appropriate power source.
Key Considerations:
Avoid Interference: Ensure that wiring doesn’t create electrical interference that might affect the sensor's readings.
Weatherproof Connections: Use weather-resistant connectors and cables to protect the sensor and power supply from the elements.
Check Power Source:
Some sensors are powered by solar panels, while others require a standard electrical connection. Make sure the power source is reliable and consistent.
Once the sensor is installed, calibration is an essential step in ensuring its accuracy. Calibration allows the sensor to provide precise readings of solar radiation.
Steps for Calibration:
Refer to the Manufacturer’s Instructions:
Each sensor may have its own calibration procedure, so always follow the guidelines provided by the manufacturer.
Check Zero Calibration: Ensure the sensor’s readings are zeroed when it is in the shade or completely out of sunlight.
Adjust for Location:
You may need to adjust the sensor based on where you live. This helps account for local weather, altitude, or seasonal changes.
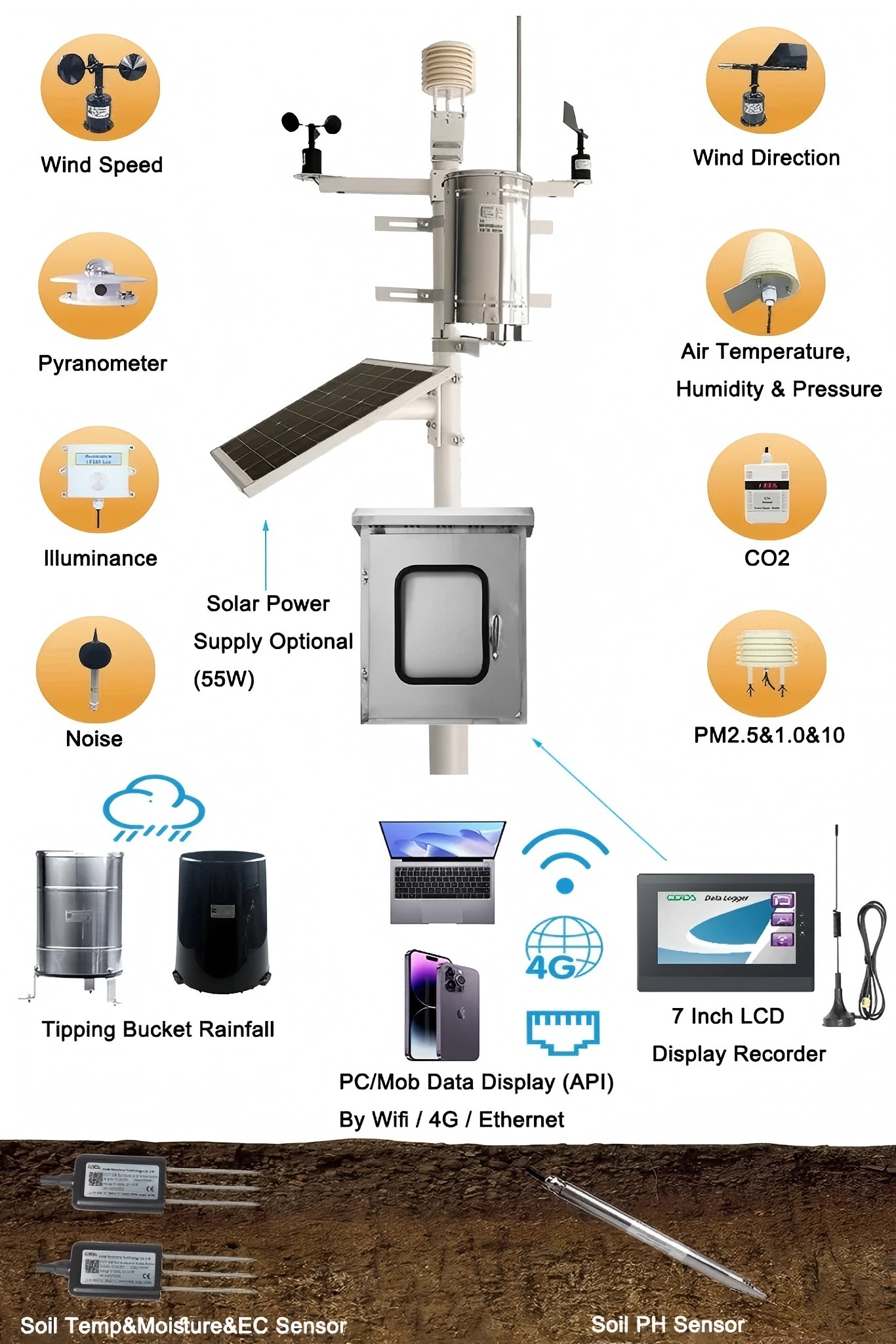
After installation and calibration, the next step is to integrate the sensor into a data logging or monitoring system. Many modern solar radiation sensors work with cloud-based platforms or IoT systems. These systems allow for real-time data collection and analyzing.
Integration Tips:
Connect to Cloud-Based Platforms:
If your sensor supports wireless connectivity, integrate it with a cloud-based monitoring system to access data remotely.
Use Data Loggers: For wired sensors, use a compatible data logger to store and transmit data.
Set Up Alerts:
Many systems let you set up alerts for unusual solar radiation levels. This includes readings that are too low or too high.
To keep things running well, regular maintenance is important. Clean the sensor and check its alignment often. If using wireless sensors, ensure that the communication signal is strong and stable.
Maintenance Tips:
Clean the Sensor:
Dust, dirt, and other debris can affect sensor accuracy, so make sure the sensor is cleaned regularly.
Check for Wear:
Over time, mounting hardware may loosen, so it’s important to check the sensor’s physical condition regularly.
Verify Data Accuracy: Compare sensor data with external sources, such as weather stations, to ensure the readings are accurate.
Inaccurate Readings: If the sensor isn’t providing accurate data, check for obstructions or misalignment. Also, make sure to calibrate the sensor properly.
Sensor Not Connecting:
If using wireless sensors, check the strength of the wireless signal and make sure the device is within range of the receiver or gateway.
Power Issues:
Ensure that the sensor is properly connected to a reliable power source, and that any batteries are fully charged.
Proper installation of a solar radiation sensor is crucial for obtaining accurate, reliable data for various applications, from solar energy systems to agricultural management. To make sure the sensor works well, follow these steps.
Begin by selecting an ideal spot. Afterward, firmly attach the sensor. Finally, link it to the appropriate power supply.
Subsequently, adjust the device settings. Ultimately, connect it to your monitoring system. Consistent upkeep will ensure your sensor remains in excellent shape, delivering precise solar radiation measurements for many years ahead.
If you need good solar radiation sensors, check out Coda Sensor. They offer a variety of solutions for solar energy and environmental needs.
In the era of precision agriculture, the efficie
Discover how online pH sensors improve smart agr
Choosing the right online pH sensor is critical
Contact: Molly
Phone: +86-17775769236
Tel: 86-0731-85117089
Email: molly@codasensor.com
Add: Building S5, Aux Square, Yuelu District, Changsha City, Hunan Province, China
We chat