With increasing global connectivity, sensors are becoming part of the Internet of Things (IoT). This change is transforming how we watch and manage environmental conditions.
Solar radiation sensors measure how much sunlight hits the Earth's surface. They are important tools for solar energy systems, farming, and environmental monitoring.
Putting these sensors into IoT systems helps collect data in real-time. It also allows for remote monitoring and automatic adjustments. This gives users useful insights and boosts efficiency.
In this article, we will explain how to connect a solar radiation sensor to an IoT system. This will help with smooth data flow, easy monitoring, and automation.

Before we begin the integration process, let's discuss the benefits of connecting a solar radiation sensor to IoT systems. This connection can provide valuable data and insights.
Remote Monitoring: Integrating IoT enables users to track solar radiation levels live from any locati0n, minimizing the necessity for manual checks.
Data Accessibility: The solar radiation sensor sends data to a central platform. There, the data can be analyzed and visualized. This helps in making better decisions.
Automation: IoT systems can automate tasks using solar radiation data. For example, they can change shading in greenhouses or adjust solar panel positions in solar farms.
Data Logging: Ongoing data recording helps collect past data. This data can be used to analyze trends, predict performance, and plan maintenance activities.
Energy Efficiency: Integrating solar radiation sensors into IoT systems helps optimize energy use by enabling automatic adjustments based on sunlight intensity.
The first step in the integration process is selecting a solar radiation sensor that is compatible with IoT systems. Make sure the sensor has the following features:
Wireless Communication: Many modern solar radiation sensors have wireless options like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or LoRaWAN. This makes it easier to connect to IoT networks.
Data Output Compatibility:
Ensure that the sensor's data output, whether analog, digital, or Modbus, is compatible with your IoT platform or gateway.
Accuracy and Range:
Select a sensor that gives accurate readings for your needs, like solar energy or farming. Make sure it has a good measurement range.
The next step is to choose an IoT platform or gateway. This will receive and process data from the solar radiation sensor. This platform acts as the central hub for managing sensor data and enabling communication between devices. Some important considerations when choosing an IoT platform include:
Cloud-Based Platforms:
Many IoT platforms use the cloud. This lets you access and manage your sensor data from any device with internet. Examples include platforms like ThingSpeak, AWS IoT, or Google Cloud IoT.
Local Gateways:
To process data locally or if you have connection issues, you can use an IoT gateway. This device collects data from many sensors and sends it to a local server or cloud service.
Integration Capabilities:
Make sure the IoT platform can work with the communication protocol of your solar radiation sensor. This might be MQTT, HTTP, or Modbus.
Once you’ve selected the sensor and the IoT platform, it’s time to establish the connection between the two. The process will depend on the type of communication (wired or wireless) the sensor supports.
Set Up the Wireless Network:
Set up the wireless network on the solar radiation sensor. Make sure it connects to the same network as the IoT gateway or platform.
Pair the Sensor with the IoT Platform: Use the IoT platform's pairing process to link the sensor to the network. You might need to scan a QR code, enter the device's MAC address, or change network settings in the platform’s interface.
Verify the Connection: Once paired, verify that the sensor is transmitting data correctly to the IoT platform. This can be done through the platform’s dashboard or monitoring interface.
Connect the Sensor to the IoT Gateway:
Use the correct cables to connect the solar radiation sensor. You can use RS485, Modbus, or analog outputs. Connect these to the IoT gateway or data logger.
Configure the Gateway: Set up the gateway to collect data from the sensor and send it to the IoT platform. This may require configuring the gateway’s communication protocol and data format.
Test the Data Flow:
After you set up the connection, test the data flow. Check that the sensor sends readings to the platform correctly.
Once the sensor is connected, configure the IoT platform to collect, store, and visualize the solar radiation data. This typically involves:
Setting Up Data Logging:
Ensure that the sensor data is being logged at regular intervals (e.g., every minute or hour). This data can be stored in the cloud or on a local server.
Visualization:
Use the IoT platform’s dashboard to create visualizations (charts, graphs, etc.) that display solar radiation levels over time. This allows for easier monitoring and decision-making.
Alerts and Notifications: Set up automated alerts based on specific solar radiation thresholds. You can set an alert if solar radiation goes above a certain level. This suggests there may be too much sunlight in a greenhouse or an issue with a solar panel.
One main benefit of using solar radiation sensors with IoT systems is automating actions based on real-time data. For instance:
Solar Farm Applications: Automatically adjust the orientation of solar panels based on solar radiation readings to optimize energy capture throughout the day.
Greenhouse Applications: Automate shading systems or adjust artificial lighting based on solar radiation levels to optimize plant growth conditions and reduce energy consumption.
Environmental Monitoring: Trigger other environmental sensors or systems to adjust temperature, humidity, or air quality based on solar radiation readings.
To ensure continuous and reliable operation, it’s essential to maintain the IoT system and solar radiation sensors:
Firmware Updates:
Update the firmware of the sensors and IoT platform regularly. This keeps them running the latest software and security patches.
Sensor Calibration:
Regularly check the sensor to keep it accurate. This is important if it is in tough environments.
Monitor Performance:
Regularly observe system performance via the IoT platform to detect any problems with sensor data or connectivity.
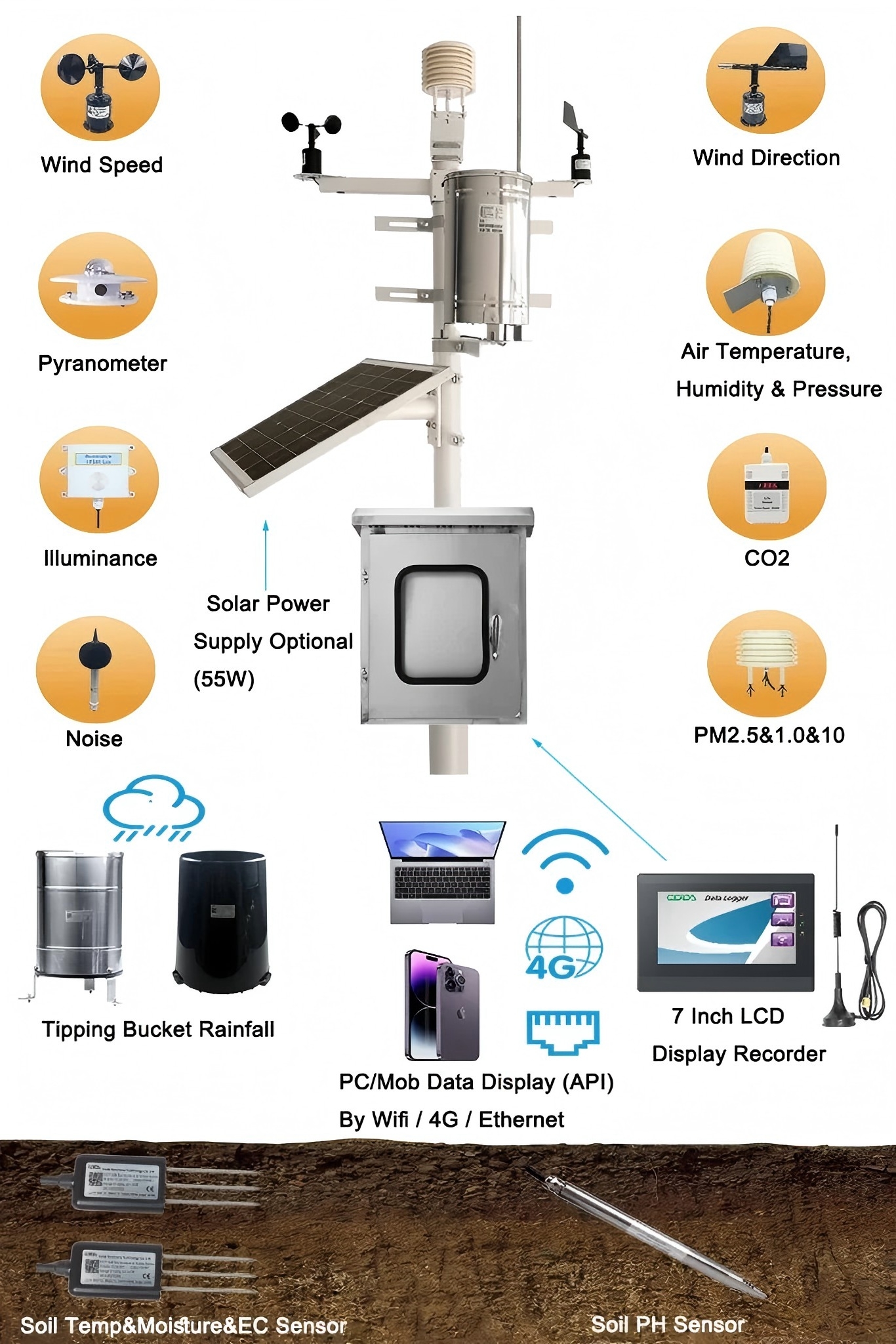
Combining a solar radiation sensor with an IoT system creates many opportunities. It lets you monitor things in real-time, analyze data, and automate tasks.
By following the steps in this guide, you can improve your solar energy systems, farming, or environmental monitoring. Begin by selecting the appropriate sensor, then link to an IoT platform. Next, set up data collection and automate responses.
Coda Sensor provides high-quality solar radiation sensors. These sensors work well with IoT systems. They give accurate data and perform efficiently for your needs.
In the era of precision agriculture, the efficie
Discover how online pH sensors improve smart agr
Choosing the right online pH sensor is critical
Contact: Molly
Phone: +86-17775769236
Tel: 86-0731-85117089
Email: molly@codasensor.com
Add: Building S5, Aux Square, Yuelu District, Changsha City, Hunan Province, China
We chat