Every time your smartphone screen automatically brightens in sunlight or dims in a dark room, an illuminance sensor is at work. These remarkable devices - often called lux sensors - serve as the "eyes" of our increasingly smart environments, quietly measuring visible light to make our world more comfortable, efficient, and sustainable.
From the office buildings where we work to the greenhouses growing our food, illuminance sensors play a crucial role in optimizing light levels. They measure light intensity in lumen per square meter (lux), providing the data that smart systems use to adjust lighting conditions automatically. This technology helps reduce energy waste in cities, improves crop yields in agriculture, and even regulates the light that affects our circadian rhythms.
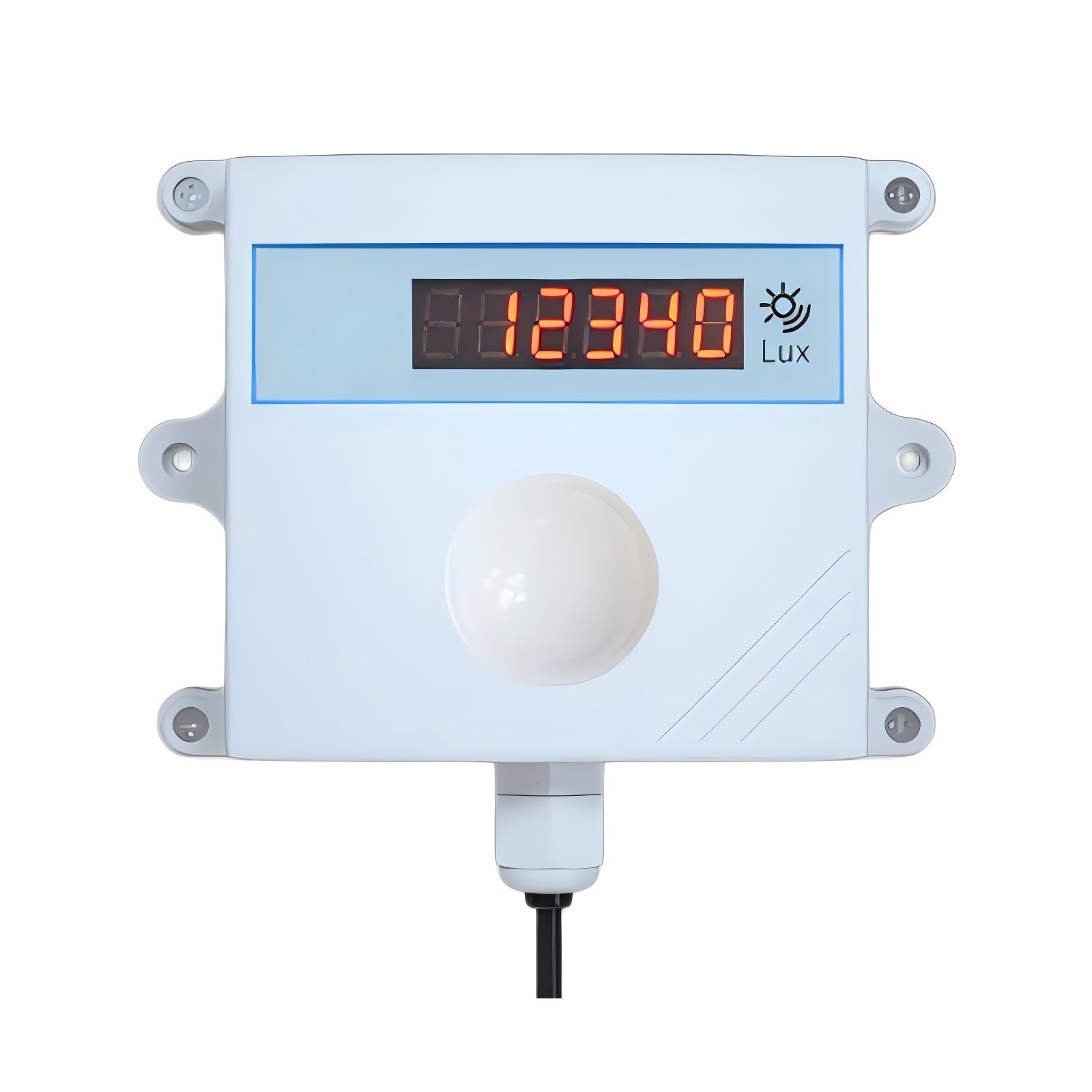

What makes modern illuminance sensors so remarkable is how they mimic human vision. Like our eyes, these sensors are specifically tuned to the visible light spectrum (400-700 nanometers). Their spectral sensitivity closely matches the human eye's response to different colors of light, meaning they "see" brightness much the way we do.
This human-centric design is crucial because:
• It ensures lighting feels natural and comfortable
• It provides measurements that correlate with human perception
• It helps create environments that support our biological needs
When we ask "what does an illuminance sensor sense," we're really exploring a sophisticated system that:
Captures light through specialized photodiodes or light dependent resistors
Filters the light to match human visual sensitivity
Measures intensity across a huge range - from faint starlight (0.01 lux) to bright sunlight (100,000 lux)
Compensates for temperature changes that could affect accuracy
Converts the data into usable digital signals
This entire process happens continuously and automatically, allowing real-time adjustments to lighting conditions.
Modern office buildings now use networks of illuminance sensors to create perfect lighting conditions while saving energy. These systems:
• Blend natural and artificial light seamlessly (daylight harvesting)
• Adjust throughout the day to support worker alertness
• Respond to occupancy to light only occupied spaces
• Can reduce lighting energy use by 50-70%
The Edge in Amsterdam, considered the world's smartest office building, uses over 6,500 connected sensors to achieve unprecedented efficiency while creating an ideal work environment.
In greenhouses and vertical farms, illuminance sensors help:
• Optimize grow lights to specific crops' needs
• Maintain ideal light levels for each growth stage
• Reduce energy use while maximizing yields
• Automatically adjust for changing weather conditions
Farmers using this technology report both higher quality crops and significant energy savings - sometimes cutting lighting costs by 40% while improving yields.
Urban areas worldwide are implementing smart street lighting that:
• Automatically brightens when pedestrians approach
• Dims during low-traffic periods
• Provides perfect visibility while minimizing light pollution
• Alerts maintenance crews before lights fail
These systems, powered by illuminance sensors, are making cities safer while reducing municipal energy bills by millions of dollars annually.
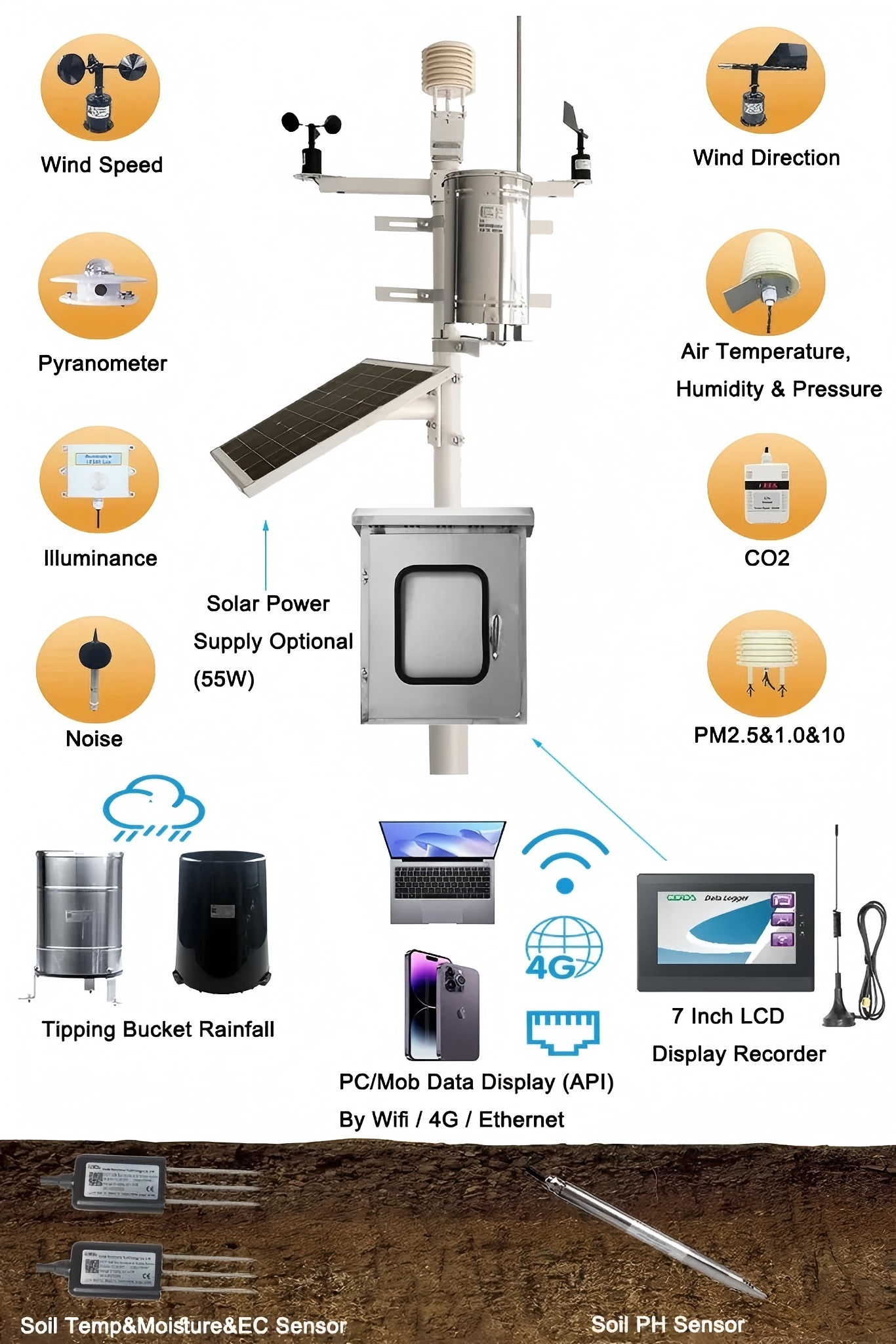
With various sensor types available, consider:
Measurement range needed for your application
Required accuracy and response time
Environmental conditions (outdoor/indoor, temperature ranges)
Output options (analog signals vs. digital connectivity)
Special features like waterproofing or wireless capability
To get the most accurate measurements:
• Mount sensors away from shadows and reflections
• Ensure proper orientation (many need a clear "view" of the area)
• Consider height and angle relative to light sources
• Protect from extreme weather when used outdoors
• Plan for periodic calibration checks
Emerging technologies are taking illuminance sensing to new levels:
• AI-powered systems that predict lighting needs before they occur
• Multi-spectral sensors that measure beyond visible light
• Self-powered designs that harvest energy from ambient light
• Tiny, inexpensive sensors enabling widespread deployment
These advancements promise even smarter environments that automatically create perfect lighting conditions while using minimal energy.
Illuminance sensors represent one of those transformative technologies that work quietly in the background, making our world function better. From the buildings where we live and work to the farms growing our food and the cities we move through, these devices are helping create environments that are:
• More energy efficient
• More comfortable and healthy
• More responsive to human needs
• More sustainable for future generations
As this technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative applications that will further improve how we interact with light in our daily lives. The future looks bright - and perfectly illuminated.
In the era of precision agriculture, the efficie
Discover how online pH sensors improve smart agr
Choosing the right online pH sensor is critical
Contact: Molly
Phone: +86-17775769236
Tel: 86-0731-85117089
Email: molly@codasensor.com
Add: Building S5, Aux Square, Yuelu District, Changsha City, Hunan Province, China
We chat