Over half of the world's population now lives in cities—and by 2050, this number is expected to reach nearly 70%. With this rapid urbanization comes a surge in challenges: air pollution, noise pollution, traffic congestion, and declining public health. Traditional city infrastructure often lacks the agility to respond to these issues in real time.
Enter the concept of the smart city—an urban area that uses digital technology, sensor networks, and intelligent analytics to enhance quality of life, operational efficiency, and sustainability. Among the many technologies enabling this transformation, noise sensors and air quality sensors play a vital role.
A smart city integrates information and communication technologies (ICT) into its infrastructure and services. This includes energy grids, transportation systems, waste management, and environmental monitoring. The goal? To optimize resource usage, reduce environmental impact, and improve the health and safety of residents.
Environmental sensing is at the core of this system—providing the data needed for decision-making, policy enforcement, and community engagement.
Noise pollution is one of the most underestimated public health threats in modern cities. Prolonged exposure to high noise levels—especially from traffic, construction, and industrial activities—can lead to sleep disorders, stress, cognitive impairment in children, and even cardiovascular disease.
Noise sensors detect and record sound pressure levels (in dB) continuously, providing real-time information on noise intensity and frequency. These devices can be installed on lamp posts, buildings, public transport stations, or integrated into IoT networks.
24/7 Monitoring: Track noise fluctuations day and night across different city zones.
Source Identification: Determine whether noise is coming from traffic, aircraft, nightlife, or industrial zones.
Compliance and Enforcement: Help authorities enforce local noise regulations with clear, timestamped data.
Urban Planning: Aid in the design of noise barriers, zoning regulations, or road reconfigurations.
Smart Traffic Systems: Adjust speed limits and reroute traffic based on noise thresholds.
Event and Venue Management: Monitor concerts, sports events, or nightlife districts for sound compliance.
Quiet Zone Creation: Designate hospital zones, parks, or residential areas as “low-noise” zones, supported by sensor data.
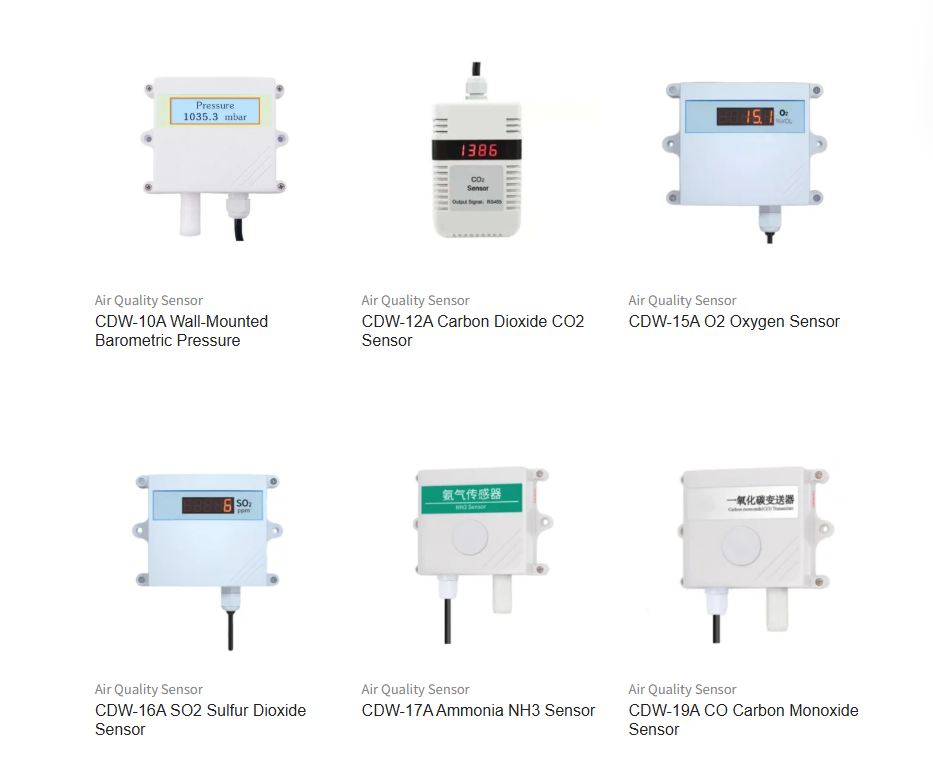

Air pollution is a leading cause of respiratory disease, cardiovascular issues, and premature deaths worldwide. In cities, pollutants like PM2.5, PM10, NO₂, O₃, CO, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are produced by vehicles, industry, construction, and even household heating.
These compact, intelligent devices detect concentrations of multiple pollutants and transmit the data in real time to a central cloud platform or control center. Many modern air quality sensors also measure temperature and humidity to contextualize pollution data.
Real-Time Alerts:
Notify residents and city authorities when air quality becomes unhealthy.
Pollution Mapping:
Create hyper-local pollution maps to identify hot spots.
Policy Support:
Provide data for implementing low-emission zones, public transit incentives, and industrial regulation.
Public Awareness:
Allow citizens to check current air quality through mobile apps or digital displays.
Smart Schools: Monitor air inside and outside school campuses to protect children’s health.
Construction Monitoring: Detect dust and emissions from ongoing construction projects.
Traffic and Emission Control: Adjust traffic lights or limit vehicle entry in high-pollution areas.
Smart cities thrive on data integration. When noise sensors and air quality sensors are combined into a single platform, cities gain a powerful environmental management tool.
Imagine a high-traffic intersection where both noise and air quality readings spike during peak hours. With real-time insights, the city can:
Deploy adaptive traffic signals to ease congestion.
Implement low-emission zones during peak times.
Enforce quiet hours in residential districts.
Inform citizens to avoid outdoor activities or wear masks when air quality is poor.
This level of integration not only improves environmental quality but also builds public trust by making data transparent and actionable.
Barcelona’s smart city initiative includes an extensive sensor network monitoring air pollution and noise. The city uses this data to control traffic lights, manage public transport schedules, and provide real-time information to residents.
Singapore leverages environmental sensors across the city to support its Smart Nation vision. Data from air quality and noise sensors informs ventilation systems, construction planning, and public health warnings.
Seoul’s city government has implemented smart sensors in sensitive areas like schools and elderly care centers, ensuring environmental safety for the most vulnerable groups.
While the technology is advanced, cities must address challenges such as:
Data Privacy: Ensuring sensor data does not infringe on personal privacy.
Infrastructure Investment: Balancing cost with long-term sustainability.
Data Management: Handling vast volumes of real-time data efficiently.
Public Engagement: Encouraging citizens to participate in and trust smart systems.
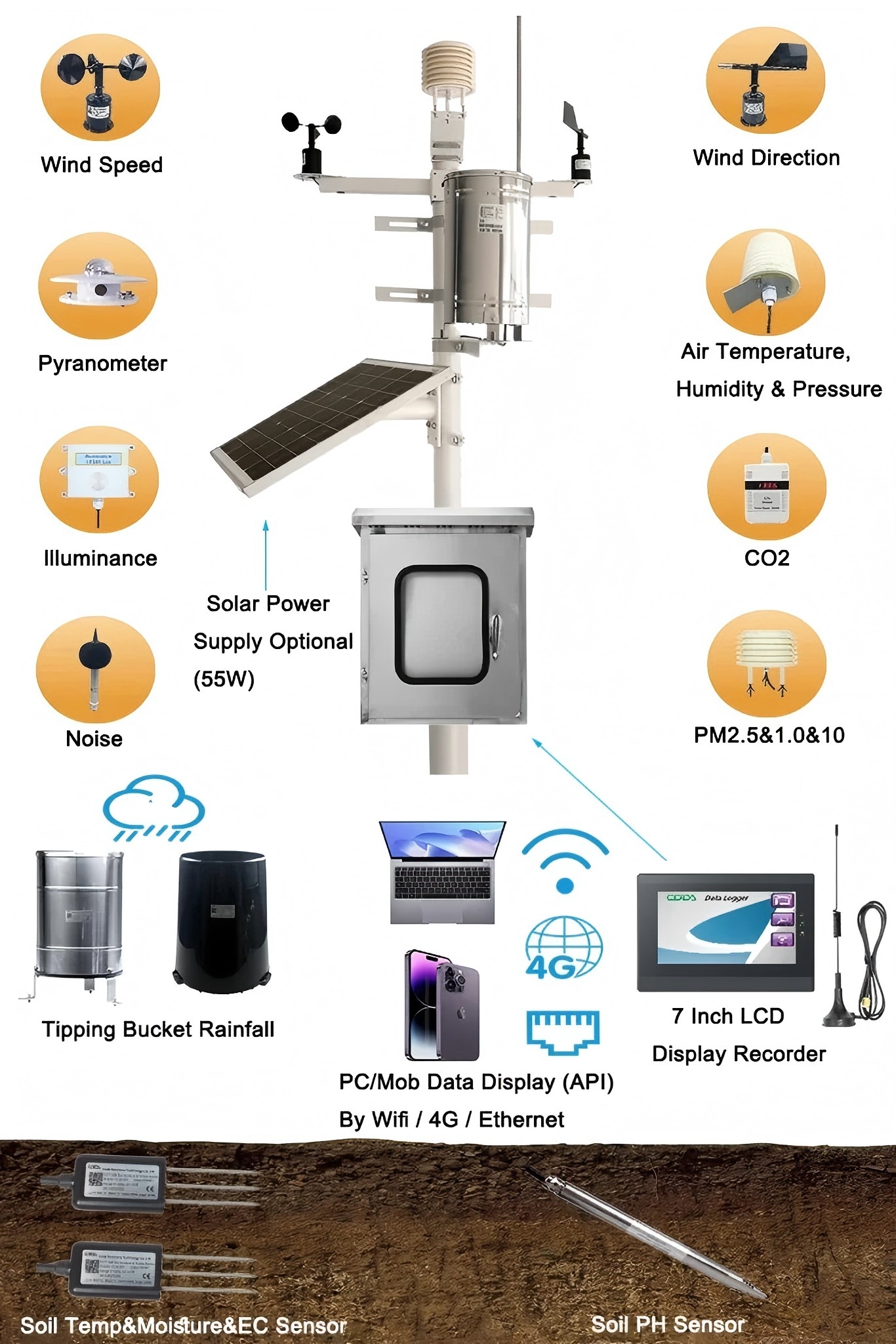
The integration of noise sensors and air quality sensors is redefining how cities approach environmental management. These devices serve as the city’s sensory organs—providing real-time insights that allow for smarter, faster, and more effective decisions.
In the era of climate change and rapid urbanization, environmental data isn’t just helpful—it’s essential. For cities aiming to be safer, greener, and more livable, smart environmental sensors are no longer optional—they are foundational.
In the era of precision agriculture, the efficie
Discover how online pH sensors improve smart agr
Choosing the right online pH sensor is critical
Contact: Molly
Phone: +86-17775769236
Tel: 86-0731-85117089
Email: molly@codasensor.com
Add: Building S5, Aux Square, Yuelu District, Changsha City, Hunan Province, China
We chat