We should comprehensively consider various points for the ambient weather station installation. Firstly, we need to select sites reasonably according
to the geographical environment and requirements. Secondly, we should take into account the characteristics of transmission methods like wired Ethernet
(considering its stable transmission but the limitation of wiring by geography and high cost) and 4G network (wide coverage which is beneficial to multi-
regional deployment).To learn more about install weather station, continue reading this article.
We also have to ensure that the data acquisition equipment can be connected to a variety of terminal devices (such as computers, smartphones and tablets)
through WIFI to make data reception and processing convenient. Moreover, we should consider the possible influence of bad weather on signal and transmission.
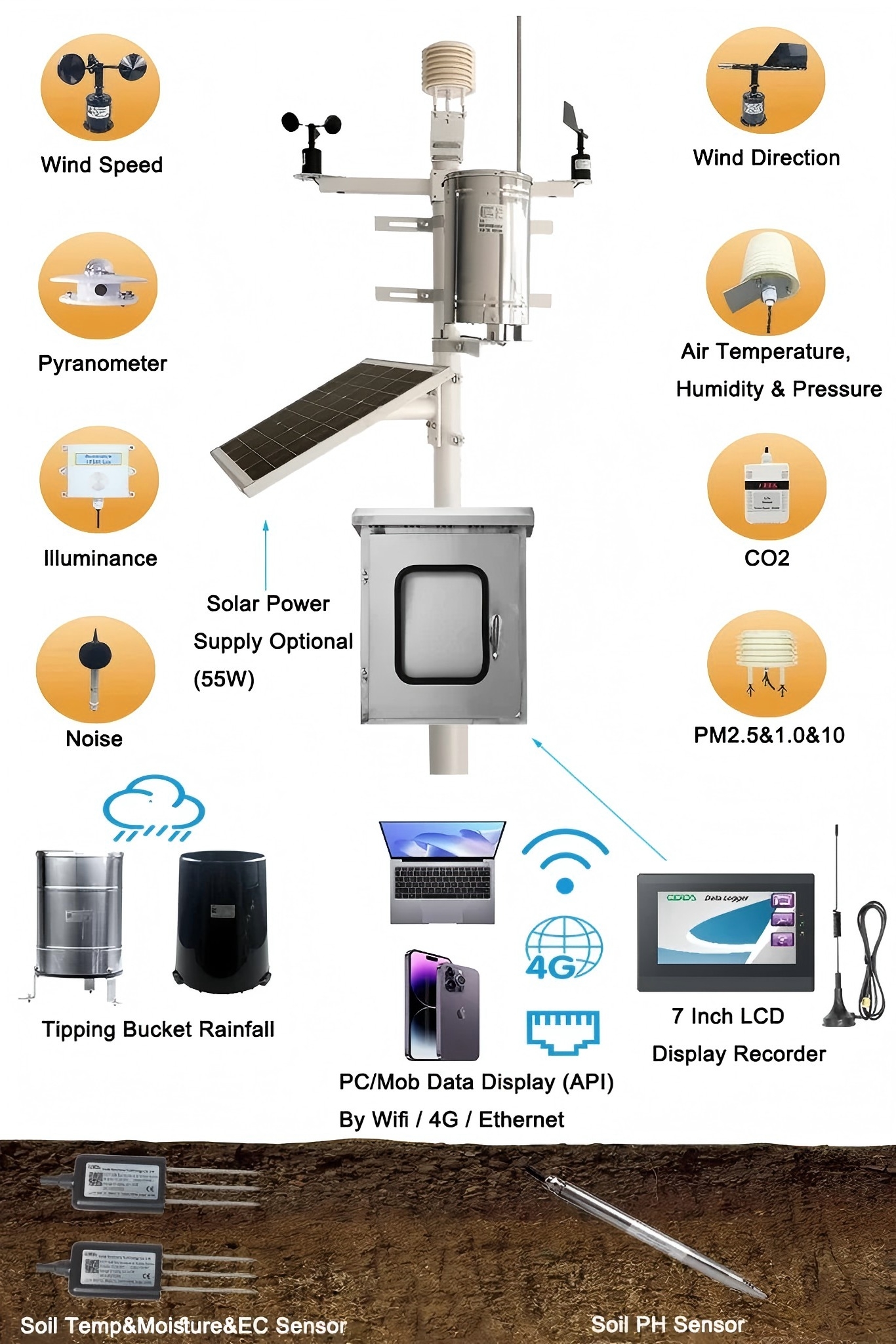
CDQ-T0C Professional Weather Station
When install weather station, it is of utmost importance to pick an open and spacious area. Such an area needs to be far away from all kinds of obstructions
like buildings, trees or other edifices. These obstructions could interfere with the normal wind patterns and also have an impact on the precision of temperature
and humidity measurements.
The chosen ambient weather station installation location must be characteristic and typical of the encompassing environment, devoid of any heat-emitting
elements or sources of excessive moisture. Such elements could introduce biases in the measured temperature and humidity values, leading to inaccurate data.
Should preferably install the weather station on flat and even ground. This not only helps in preventing the accumulation of water, which could damage the
equipment, but also guarantees the stability and proper functioning of the station, ensuring the reliability of the collected meteorological data.
Mounting the Weather Instruments:
Position the anemometer, the sensor for detecting wind speed and direction, at an elevation above the ground that allows it to sample wind flow without any
blockages. The typical and recommended height for installing anemometers is precisely 10 meters (equivalent to 33 feet) above the ground.
Mount the temperature and humidity sensors in a shaded area to prevent direct exposure to sunlight, which can affect readings.
Power Supply:
Choose the power supply for your weather station. Some use batteries, while others need mains power or a solar panel for continuous running.
Ensure the power source is reliable and protected from environmental factors such as moisture and temperature extremes.
Lighting conditions:
The install weather station ought to possess ample light. It is essential to steer clear of surrounding obstructions like tall edifices and trees. This is to guarantee
the precise measurement of solar radiation quantity. Given that solar radiation data holds significant importance in evaluating the efficiency of photovoltaic power
generation.
Representative area:
Select the location that can represent the meteorological conditions of the region where the photovoltaic power station is located. If the photovoltaic power
station area is large, we had better install the weather station in the central area of the power station or the area near the main power generation equipment.
Avoid interference sources:
Keep away from large heat sources, pollution sources, and electromagnetic interference sources.
Photovoltaic panel Angle matching:
Ideally, the installation plane of the radiation sensor should be consistent with the installation plane of the photovoltaic panel. For fixed Angle photovoltaic
panels, the sensor should also be installed at the same Angle.
The radiation sensor should be installed at an appropriate height, generally 1.5 – 2 meters above the ground. This height can avoid ground – related interferences
like reflection and thermal radiation on measurement results, and also simplifies daily maintenance and inspection.
Installing a weather station requires careful planning and attention to detail to ensure accurate data collection and reliable operation. Here’s a comprehensive
guide on how to set up and install a weather station, taking into account geographic, climatic, and technical considerations.
**1. Site Selection**
- Choose a suitable location based on the surrounding geography and measurement objectives. Prioritize open and unobstructed areas to avoid interference from
nearby structures such as buildings, trees, or other large objects, which can affect wind patterns and temperature readings.
- The chosen site should represent the environmental conditions of the broader area and avoid sources of heat, moisture, or other localized anomalies that can
distort measurements (e.g., asphalt surfaces, air conditioning units).
- A flat, stable surface is ideal to prevent issues like water pooling or instability during severe weather conditions.
**2. Transmission Considerations**
- Decide on the preferred data transmission method:
- **Wired Ethernet**: Offers stable and reliable transmission but may be limited by terrain and higher installation costs due to cabling.
- **4G Network**: Provides wide coverage, making it suitable for multi-regional deployments or remote areas with minimal infrastructure.
- Ensure the weather station supports wireless connectivity like Wi-Fi if frequent data access via devices such as computers, smartphones, or tablets is required.
This enhances portability and ease of use.
**3. Weather Resistance**
- Anticipate the effects of adverse weather such as rain, strong winds, or snow, which can impact both signal quality and equipment durability. Use protective
measures for electronics to prevent damage.
**1. Anemometer (Wind Speed/Direction Sensor)**
- Install the anemometer at a height of 10 meters (33 feet) above ground level in a location free from obstructions to allow for accurate wind flow measurement.
**2. Temperature and Humidity Sensors**
- Position these sensors in a shaded area to protect them from direct sunlight, which may skew readings. If possible, use a radiation shield or stevenson screen
designed specifically for meteorological equipment.
**3. Radiation Sensor (for Solar Monitoring)**
- Ensure ample sunlight exposure by avoiding nearby obstructions such as tall buildings or trees. If installed at a photovoltaic station, align the sensor’s plane
with that of the photovoltaic panels for consistency in solar radiation measurement. Mount the sensor 1.5–2 meters above the ground to mitigate interference
from ground reflections and thermal radiation.
- Select a power source based on the station's design:
- Battery-powered models are portable but require periodic battery replacement or recharging.
- Stations requiring mains power provide reliability but need robust protection against environmental exposure (e.g., waterproofing).
- Solar-powered systems are eco-friendly and ideal for remote setups but should be installed in locations with consistent sunlight.
- Ensure all power supplies are insulated and safeguarded against temperature fluctuations and moisture ingress.
- For stations using wired sensors, carefully plan cable routes to minimize tangling or exposure to environmental damage. Use cable clips or conduits to
secure wires and protect them from wear or physical impacts. Properly seal any connections to prevent corrosion or water ingress.
Special Considerations for Photovoltaic Industry Weather Stations
**1. Lighting Conditions**
Ensure uninterrupted access to sunlight when installing near photovoltaic systems, as accurate solar radiation measurements are vital for evaluating energy
generation efficiency.
**2. Placement in Representative Areas**
Install the weather station in a location that reflects the typical meteorological conditions of the region. In large photovoltaic installations, positioning it near
key equipment or central areas ensures accuracy.
**3. Avoidance of Interference Sources**
Keep the station away from heat-emitting devices, pollution sources, or electromagnetic fields that could distort readings.
**4. Matching Panel Angles**
Align radiation sensor angles with those of fixed photovoltaic panels to ensure consistent measurement results.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure the proper installation of your weather station, whether it’s for general environmental monitoring or
specialized purposes like photovoltaic systems.
**CDQ-T0C Hydrological Monitoring Weather Station**
**Proximity to Water Bodies:**
Weather stations should be installed as near as possible to the water body being monitored, such as riverbanks, lake shores, or reservoir edges. This
positioning allows for precise collection of meteorological data related to water evaporation and precipitation directly affecting these water bodies.
**Site Representativeness:**
The chosen installation site should accurately reflect the meteorological conditions of the entire hydrological monitoring zone. For large reservoirs, ideal
locations include a central peninsula or an open shoreline. This ensures the collection of reliable data, such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, and
direction, which can be applied to hydrological modeling across the reservoir.
**Waterproof and Moisture Protection:**
Given their proximity to water bodies, equipment must be adequately waterproof and moisture-proof. All electrical components, including connection lines,
should be protected against water damage to maintain functionality.
**Stability and Durability:**
Supports and instruments should be securely installed to withstand adverse weather conditions that are common near water, such as high winds or heavy rains.
Windproof measures, like deeply embedded foundations or weighted bases, are recommended to prevent equipment from toppling under severe conditions.
**CDQ-T0C Smart Agricultural Weather Station**
**Representative Field Area:**
The weather station should be placed to reflect the prevailing meteorological conditions of the entire farmland. For large-scale fields, the ideal location is at
the center of the field or near major crop-growing areas.
**Avoid Obstacles and Interference:**
Install the station in a location free from obstruction by tall buildings, trees, or other structures to ensure accurate measurements of solar radiation, precipitation,
wind direction, and wind speed.
**Proximity to Irrigation and Drainage Systems:**
To facilitate monitoring of precipitation and irrigation effects on soil moisture, the station should be placed close to irrigation sources and drainage channels.
This placement supports better integration of meteorological data with irrigation and drainage system management.
**Sensor Installation Height:**
- **Temperature and Humidity Sensors:** These should be installed at a height of 1.5–2 meters above the ground, close to the crop canopy, to accurately
capture growing conditions.
- **Rain Sensor:** Its rain socket should be mounted at 0.7–1 meter above ground level to minimize interference from splashes during rainfall.
**CDQ-T0C Environmental Weather Station**
**Representative Environmental Locations:**
Weather stations should be installed where environmental conditions represent the broader surroundings. In urban environments, a mixed-use area
combining residential, commercial, and light industrial zones is ideal for obtaining comprehensive data that reflects the city’s overall meteorological
profile.
**Distance from Pollution Sources:**
The station must be sited away from major pollution sources, including industrial sites (chemical plants, incinerators), high-traffic areas (busy highways,
railways), and agricultural zones with intensive pesticide or fertilizer use. This ensures untainted data collection.
**Topographical Considerations:**
Flat and open terrains are preferred for station placement. Avoid installing in valleys or on steep slopes, as these areas may accumulate pollutants or
experience airflow convergence that skews readings.
**Installation Heights:**
- **Temperature and Humidity Sensors:** These should be installed 1.5–2 meters above ground level to mitigate interference from ground radiation
and water vapor while aligning with typical human activity heights.
- **Air Quality Sensors:** The air intakes for these devices should be positioned 3–5 meters above ground level to capture representative atmospheric
pollutant concentrations without interference from ground-level dust or emissions.
In the era of precision agriculture, the efficie
Discover how online pH sensors improve smart agr
Choosing the right online pH sensor is critical
Contact: Molly
Phone: +86-17775769236
Tel: 86-0731-85117089
Email: molly@codasensor.com
Add: Building S5, Aux Square, Yuelu District, Changsha City, Hunan Province, China
We chat